Name the Glycosidic Bond Occuring in This Disaccharide.
Part A Name the glycosidic bond occuring in this disaccharide CH2OH он он HO CH2 он он O β 1-1glycosidic bond a 1--6 glycosidic bond 0 ß 1-6 glycosidic bond a 1 1 glycosidic bond Submit uest Ans. Disaccharide of two glucose molecules via 1--4 glycosidic bond.
12 6 Disaccharides Chemistry Libretexts
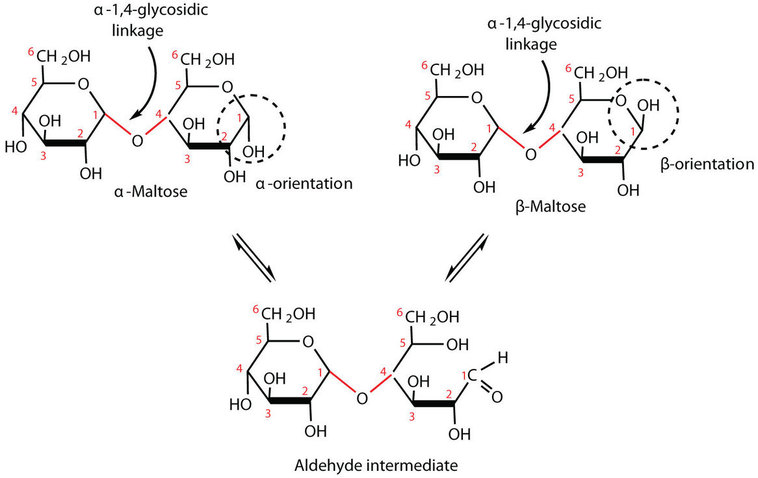
-still reducing sugar because the cyclic hemiacetal end is in equilibrium with open chain form.

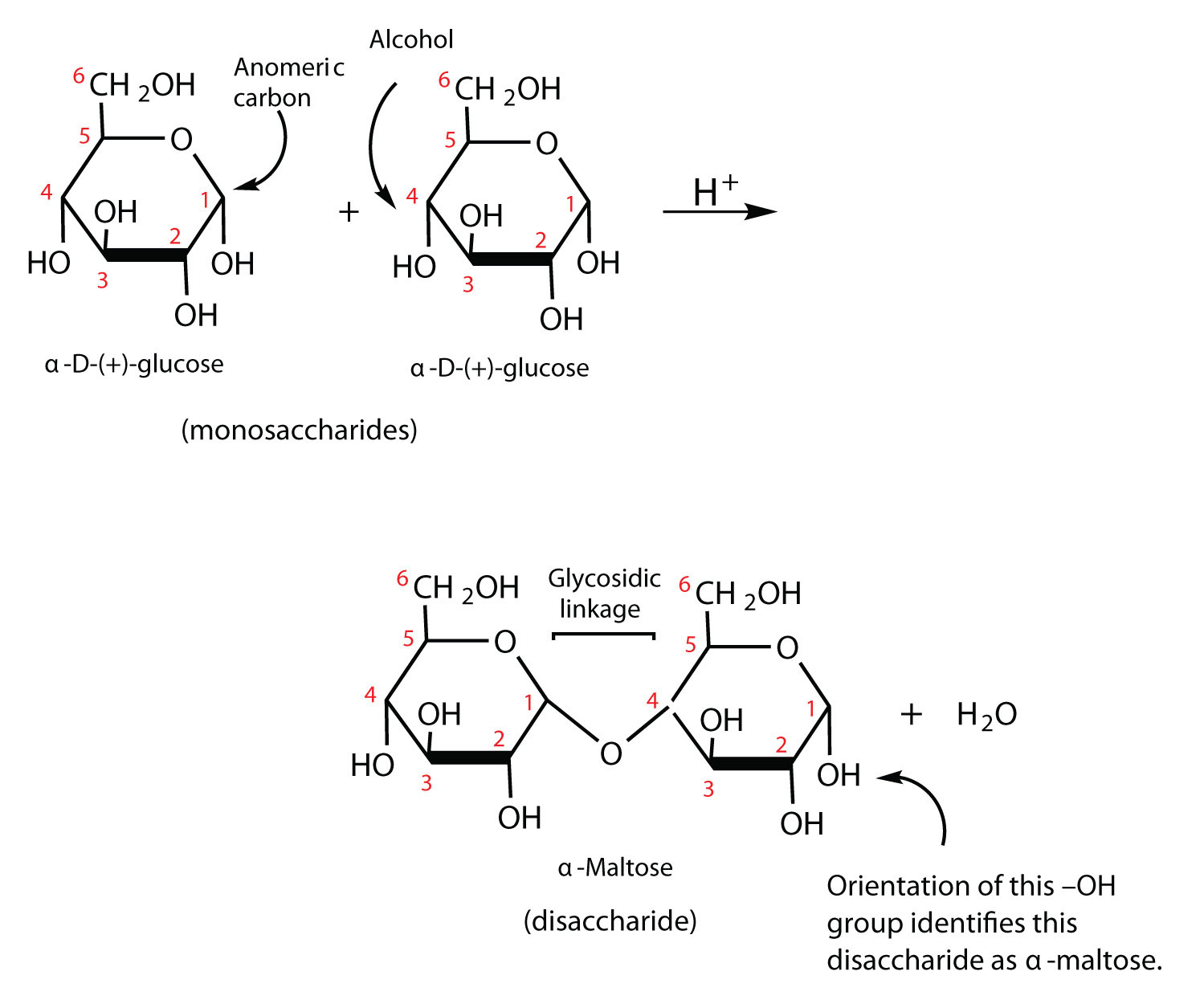
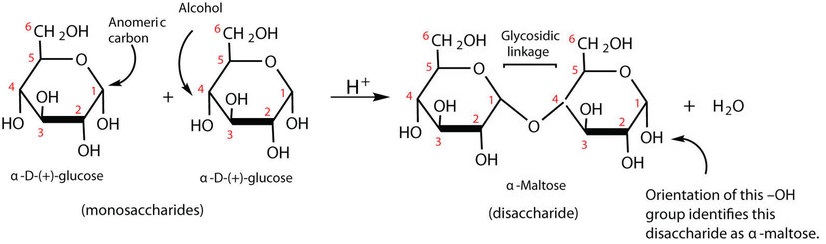
. Sugars with free anomeric carbons can reduce ferric Fe 3 and cupric Cu 2 ions and are called reducing sugars. These bonds are. The disaccharide formed upon condensation of two glucose molecules via a 1-4 bond is described as an alpha-d-glucopyranosyl-1-4-d-glucopyranose The common name for alpha-d-glucopyranosyl-1-4-d-glucopyranose is what.
The name of the bond between two amino acids is peptide bond. During the glycosidic bond formation one. Disaccharides A disaccharide is formed when two.
The monosaccharide units in disaccharides and also in polysaccharides are linked through a special type of covalent bond called Glycosidic bond specifically O-glycosidic bond. Implications for barnase catalysis. Which of the following disaccharides has both anomeric carbons involved in the glycosidic bond.
The most common glycosidic bonds connecting monosaccharide units are O-glycosidic bonds in which the oxygen from a hydroxyl group becomes linked to the carbonyl carbon. Makes up about 20 of starch. Page 227 Glycosidic bonds link monosaccharides into disaccharides and polysaccharides β-D-galactopyranosyl-14-β-D-glucopyranosenon-reducing end reducing end.
The glycosidic bond an acetal between monomers. Identify the glycosidic bond in each of the carbohydrates below and label it as either O-glycosidic N-glycosidic S-glycosidic or C-glycosidic. If the anomeric carbon of the sugar forms the bond with the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group in the alcohol the bond is named an O-glycosidic bond.
These bonds can occur between the carbons and -OH of the α or β isomeric forms. Disaccharides are carbohydrates containing two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond. Amylopectin A branched chain polysaccharide connected by alpha-14-glycosidic bonds that has a branch of glucose molecules attached by an alpha-16-glycosidic bond between carbon 1 of the branch and.
Disaccharides Polysaccharides and the Digestion of Polysaccharides Exam 2 STUDY. One example of an N-linked glycosidic bond is in the molecule deoxyadenosine. Full PDF Package Download Full PDF Package.
Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharide units linked together by a glycosidic bond. Chemistry questions and answers. Glycosidic bonds form when the anomeric carbon of one sugar reacts with a hydroxyl group belonging to a second sugar.
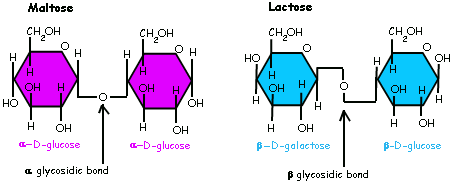
The cyclic structures of two monosaccharides form a disaccharide through Glycosidic bond or linkage. A polysaccharide that consists of 250-4000 alpha-D-glucose molecules connected by alpha-14-glycosidic bonds in a continuous chain. The bond formed between glucose and galactose monosaccharides to produce the disaccharide lactose is a β-14- glycosidic bond.
Sugars may also become linked to molecules by N-glycosidic bonds and other types of glycosidic bonds. Lactase the enzyme responsible for breaking lactose into its monomers is an _____ enzyme. Glycosidic bond is the bond that joins the monosaccharide units in a polysaccharide chain.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2007. Two sugar molecules conjoined between an anomeric carbon and a hydroxyl carbon. This bond is formed between C1 of galactose and C4 of glucose and it happens as a reduction process.
The term glycoside is now extended to also cover compounds with bonds formed between hemiacetal or hemiketal. A glycosidic bond is formed between the hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide or a molecule derived from a saccharide and the hydroxyl group of some compound such as an alcoholA substance containing a glycosidic bond is a glycoside. Glycosidic bonds join monosaccharides or longer sugar chains to other carbohydrates forming disaccharides oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
An OH group on the monosaccharide reacts with the OH group on another molecule producing water and a new O-R. However a glycosidic bond can also occur if the nitrogen atom of an amine group attacks the anomeric carbon instead. The bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides with loss of a water molecule.
The formation of glucosidic bonds in oligo- and polysaccharides will depend on the stereochemical nature of the sugars that are attached as well as on their number of carbon. In disaccharides such as maltose lactose and sucrose the most common glycosidic bond is the O-glucosidic type. Influence of Glycosidic Linkage Neighbors on Disaccharide Conformation in Vacuum.
Coupling of the guanosine glycosidic bond conformation and the ribonucleotide cleavage reaction. A glycosidic bond can form between any hydroxyl group on the monosaccharide so even if the two subunits are the same sugar there are many different combinations of bonds and. O-glycosidic bond is formed by the reaction between the hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide with the anomeric carbon atom of the other.
Disaccharides are sugars or carbohydrates made by linking two monosaccharides. The bond is formed between two adjacent monosaccharide units and it involves dehydration. Terms in this set 24 how are glycosidic bonds formed.
This occurs via a dehydration reaction and a molecule of water is removed for each linkage.
8 3 Disaccharides Chemistry Libretexts
No comments for "Name the Glycosidic Bond Occuring in This Disaccharide."
Post a Comment